When it comes to virtualization, understanding the difference between VMware sockets and cores is crucial for optimizing your infrastructure. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or just starting out in the world of virtualization, this concept plays a big role in how you configure and manage your systems. Let's dive right in and break down what these terms mean, why they matter, and how to make the most out of them in your setup.
Imagine you're building a house—your hardware is the foundation, and VMware is the blueprint that tells you how to arrange everything. Sockets and cores are like the structural supports that keep everything standing. If you don’t get the balance right, things can get messy real quick. That's why grasping the distinction between VMware sockets and cores is so important.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about VMware sockets vs cores, including their definitions, how they impact licensing, performance considerations, and much more. By the end of this article, you’ll be ready to make informed decisions about your virtual environment. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What Are Sockets and Cores?
- VMware Licensing Model: Sockets vs Cores
- Impact on Performance
- Choosing Between Sockets and Cores
- Cost Considerations
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Best Practices for VMware Sockets and Cores
- Scaling Your Infrastructure
- Future Trends in Virtualization
- Conclusion
What Are Sockets and Cores?
Alright, let’s start with the basics. If you’re new to the world of virtualization, understanding the terms "sockets" and "cores" is like learning the ABCs. Think of them as the building blocks of your server architecture. Here's a quick breakdown:
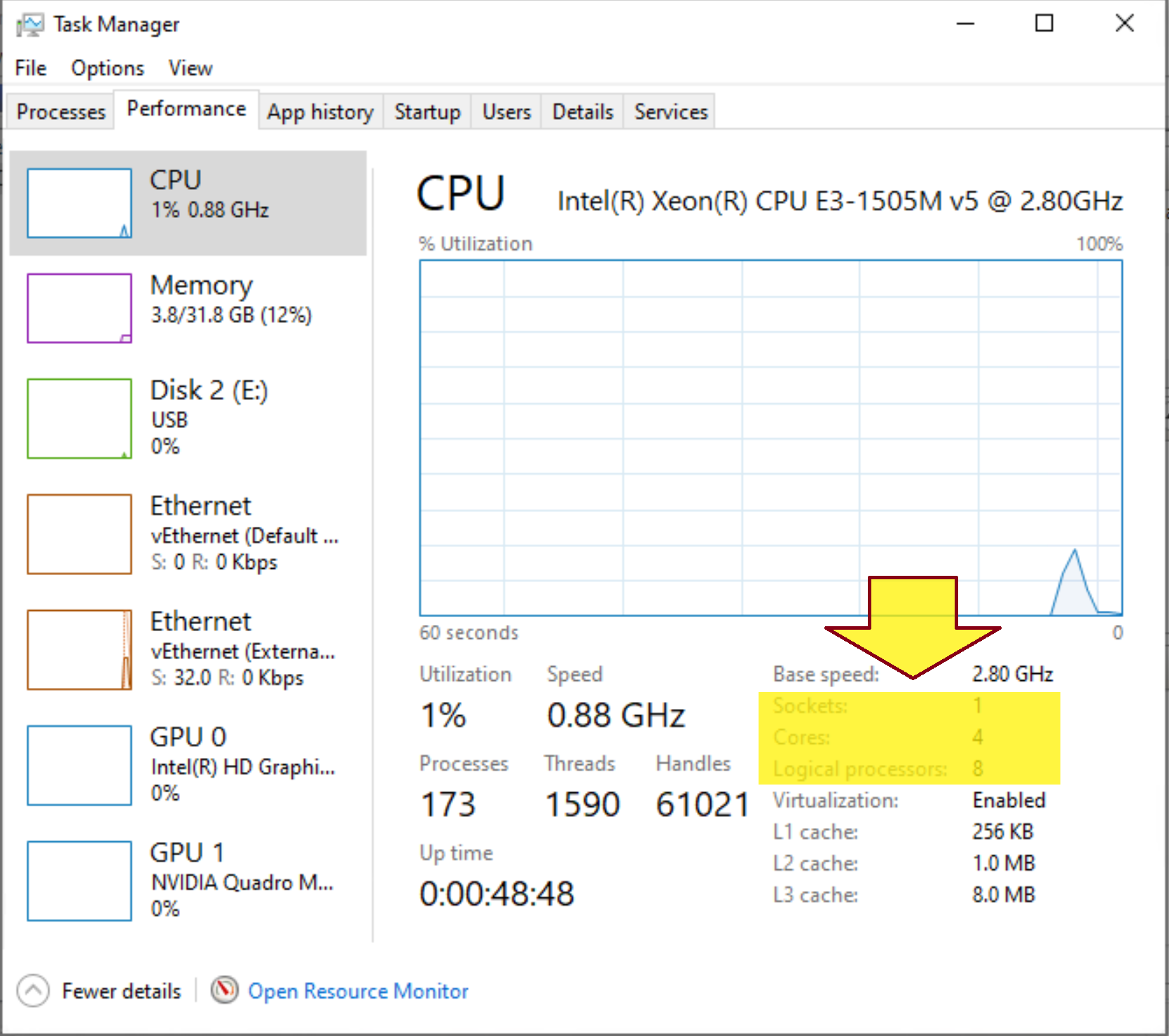
A socket refers to a physical slot on your motherboard where a CPU (Central Processing Unit) is installed. It’s like the plug where your CPU connects to the system. On the other hand, a core is a processing unit within the CPU itself. Modern CPUs often come with multiple cores, which means they can handle multiple tasks simultaneously. It's like having multiple workers in one room, each doing their own thing.
In the context of VMware, these terms are critical because they directly affect how your virtual machines (VMs) interact with the hardware. Knowing the difference helps you configure your environment more efficiently and avoid potential bottlenecks.
Why Do Sockets and Cores Matter?
Here's the thing: sockets and cores aren’t just about hardware specs—they’re also tied to licensing and performance. Let’s break it down further:
- Sockets: VMware licenses are often based on the number of physical CPU sockets in your server. This means the more sockets you have, the more you’ll pay for licensing.
- Cores: While cores don’t directly affect licensing, they play a huge role in performance. More cores mean more processing power, which translates to better VM performance.
So, understanding the balance between sockets and cores is key to getting the most out of your virtual infrastructure without breaking the bank.
VMware Licensing Model: Sockets vs Cores
Now, let’s talk about the elephant in the room—licensing. VMware’s licensing model is one of the biggest factors to consider when planning your virtual environment. Here's how it works:
VMware typically licenses its software based on the number of physical CPU sockets in your server. This means that if you have a server with two sockets, you’ll need two licenses. However, the number of cores per socket doesn’t directly impact the licensing cost. This is where things get interesting.
For example, you could have a server with two sockets, each containing a 16-core CPU. In this case, you’d still only need two licenses, regardless of the number of cores. But here’s the catch: while more cores don’t increase licensing costs, they can significantly boost performance. So, you might want to opt for fewer sockets with more cores per CPU to maximize efficiency.
How Licensing Affects Your Decision
When choosing between sockets and cores, licensing costs should be a major consideration. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Cost Efficiency: Fewer sockets with more cores per CPU can reduce licensing costs while maintaining or even improving performance.
- Scalability: If you anticipate needing more processing power in the future, opting for servers with fewer sockets but higher core counts can make it easier to scale without incurring additional licensing expenses.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to balancing performance needs with budget constraints. It’s all about finding the sweet spot that works for your organization.
Impact on Performance
Now that we’ve covered the basics of sockets and cores, let’s talk about how they impact performance. This is where things get really interesting. Performance is the name of the game in virtualization, and understanding the relationship between sockets and cores is essential for getting the most out of your setup.
Here’s the deal: more cores generally mean better performance. Each core can handle multiple threads, allowing your VMs to run more efficiently. However, the number of sockets also plays a role. Servers with multiple sockets can distribute workloads across different CPUs, which can be beneficial for certain types of applications.
Factors to Consider
When evaluating the impact of sockets and cores on performance, consider the following:
- Workload Type: Some applications benefit more from multiple cores, while others perform better with multiple sockets. Know your workloads and configure accordingly.
- Memory Bandwidth: More sockets can provide better memory bandwidth, which is crucial for memory-intensive applications.
- Latency: Fewer sockets with more cores can reduce latency, which is important for real-time applications.
At the end of the day, the best configuration depends on your specific use case. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution, so it’s important to test different setups to see what works best for your environment.
Choosing Between Sockets and Cores
So, how do you decide between sockets and cores? It’s a question that many IT professionals grapple with, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. Here are a few guidelines to help you make an informed decision:
First, consider your workload requirements. If you’re running applications that require a lot of parallel processing, more cores are probably the way to go. On the other hand, if you need better memory bandwidth or are running applications that benefit from multiple CPUs, more sockets might be the better choice.
Second, think about scalability. If you anticipate needing to expand your infrastructure in the future, it might be worth investing in servers with fewer sockets but higher core counts. This can make it easier to add more processing power without having to purchase additional licenses.
Key Considerations
Here are a few key factors to keep in mind when choosing between sockets and cores:
- Application Needs: Understand the specific requirements of your applications and configure your hardware accordingly.
- Future Growth: Plan for future expansion by selecting hardware that can scale easily.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Weigh the costs and benefits of different configurations to find the best balance for your budget and performance needs.
Remember, there’s no right or wrong answer—just what works best for your unique situation.
Cost Considerations
Let’s be real—cost is always a factor in any IT decision. When it comes to VMware sockets vs cores, the financial implications can be significant. Here’s how to approach it:
As we mentioned earlier, VMware licenses are based on the number of physical CPU sockets, not cores. This means that opting for fewer sockets with higher core counts can save you money on licensing costs. However, you also need to consider the cost of the hardware itself. Servers with fewer sockets but more cores per CPU can be more expensive upfront, so it’s important to weigh the long-term savings against the initial investment.
Another cost consideration is power consumption. Servers with more sockets can consume more power, which can add up over time. On the other hand, servers with fewer sockets but higher core counts might be more energy-efficient, which could result in lower electricity bills.
Long-Term Savings
When evaluating costs, don’t just look at the initial expense. Consider the long-term savings that can come from choosing the right configuration. Here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Licensing Costs: Fewer sockets mean fewer licenses, which can result in significant savings over time.
- Energy Efficiency: More energy-efficient servers can reduce electricity costs, which adds up over the lifespan of the hardware.
- Maintenance: Simpler configurations with fewer sockets can be easier to maintain, which can save you money on labor costs.
By taking a holistic view of the costs involved, you can make a more informed decision that aligns with your organization’s goals and budget.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even the most experienced IT professionals can make mistakes when configuring VMware environments. Here are a few common pitfalls to watch out for:
One of the biggest mistakes is not fully understanding the licensing model. As we’ve discussed, VMware licenses are based on the number of physical CPU sockets, not cores. This can lead to unexpected costs if you’re not careful. Make sure you have a clear understanding of how licensing works before making any decisions.
Another common mistake is underestimating the importance of workload requirements. Different applications have different needs, and configuring your hardware without considering these needs can lead to performance issues down the road. Take the time to analyze your workloads and configure your environment accordingly.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
Here are a few tips to help you avoid common mistakes:
- Do Your Research: Take the time to understand VMware’s licensing model and how it applies to your specific situation.
- Test Different Configurations: Experiment with different setups to see what works best for your workloads.
- Plan for the Future: Consider your long-term needs when making decisions about hardware and licensing.
By being proactive and thorough in your planning, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure a smooth-running virtual environment.
Best Practices for VMware Sockets and Cores
Now that we’ve covered the common mistakes, let’s talk about best practices. Here are a few tips to help you get the most out of your VMware environment:
First, always start with a clear understanding of your workloads. Know what applications you’re running and what their specific requirements are. This will help you configure your hardware more effectively and avoid potential performance issues.
Second, consider using VMware’s built-in tools to monitor and optimize your environment. These tools can provide valuable insights into how your VMs are performing and help you identify areas for improvement.
Additional Tips
Here are a few more best practices to keep in mind:
- Regularly Update Your Hardware: Keep your servers up to date with the latest technology to ensure optimal performance.
- Monitor Performance Metrics: Use tools like vSphere to track key performance indicators and make adjustments as needed.
- Document Your Configuration: Keep detailed records of your hardware and software configurations to make troubleshooting easier.
By following these best practices, you can create a virtual environment that’s optimized for performance and efficiency.
Scaling Your Infrastructure
As your organization grows, so will your virtual infrastructure. Scaling your environment effectively is crucial for maintaining performance and meeting increasing demands. Here’s how to do it:
First, consider your current setup. Are you using servers with multiple sockets or fewer sockets with higher core counts? Depending on your configuration, you might need to adjust your approach to scaling. For example, if